Posts
What is a plastic molding machine and how does it work?
The plastic molding machine is a critical component in the manufacturing of plastic products. It revolutionizes how items are produced, enabling high efficiency and precision. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global plastic injection molding market is projected to reach $417.6 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 5.0%. This growth reflects the increasing demand for lightweight and durable plastic parts across various industries.
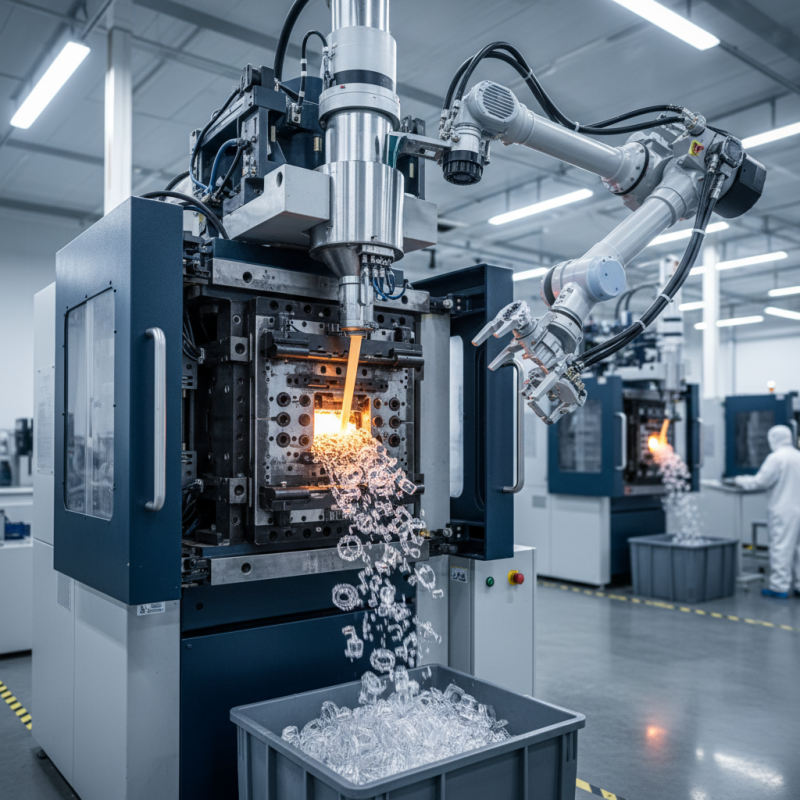
These machines operate by melting plastic pellets and injecting the molten material into molds. This process is capable of producing intricate shapes and designs with minimal waste. However, the complexity of the process can often lead to challenges in maintaining consistency and quality. Manufacturers continually seek to enhance their machinery and processes while addressing issues such as cycle times and energy consumption.
The versatility of plastic molding machines makes them essential in sectors like automotive, consumer goods, and medical devices. Yet, the rapid evolution of technology presents a constant need for adaptation. Companies must grapple with the balance between innovation and the efficiency of existing systems. Reflecting on these dynamics is crucial for those aiming to thrive in this competitive market.

What is a Plastic Molding Machine? An Overview of Its Functionality
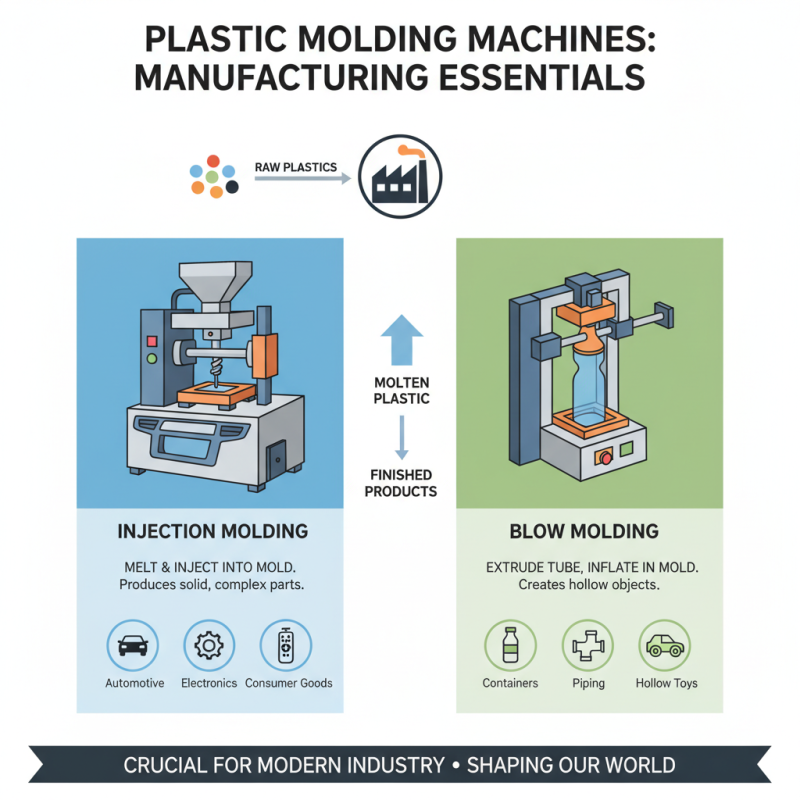
A plastic molding machine is essential in manufacturing. It transforms raw plastic into various shapes and products. This process is crucial for industries, including automotive, consumer goods, and electronics. Typically, there are two main types: injection molding and blow molding. Each method serves unique applications, influencing product design and functionality.
Injection molding dominates the market, representing over 30% of the global plastic molding industry. According to recent reports, the demand for injection-molded parts is expected to grow by 5% annually. This increase reflects the ongoing need for lightweight, durable materials in production. Blow molding, while less prevalent, is crucial for producing hollow shapes, such as bottles and containers.
Tips: When selecting a molding machine, consider energy efficiency. Machines with servo motors can save significant energy costs, up to 30%. Regular maintenance is vital to avoid production delays. Furthermore, ensure that raw materials are of high quality. Subpar materials can lead to defects in the final product, affecting profitability and reputation.
Key Components of a Plastic Molding Machine and Their Roles
A plastic molding machine is essential in manufacturing plastic products. Its efficiency hinges on key components that perform specific roles. The injection unit is crucial. It melts plastic pellets and injects the molten material into molds. This process often reaches temperatures exceeding 200°C. A survey indicated that over 70% of manufacturers prioritize this component for productivity.
The clamping unit is another vital part. It holds the mold together during injection. Proper clamping prevents leaks and ensures the final product's integrity. Clamping force can vary based on the mold size, often exceeding 1,500 tons in industrial machines. These figures highlight the importance of design and engineering.
Additionally, the cooling system contributes significantly. It removes heat from the injected plastic, allowing it to solidify. This process can take minutes, but effective cooling can reduce cycle time by 20%. However, improper cooling can lead to defects. This is an area requiring attention. The balance between speed and quality is delicate in manufacturing processes.
Plastic Molding Machine Key Components and Their Roles
The Plastic Molding Process: Steps from Material to Final Product
The plastic molding process involves several essential steps to convert raw materials into a finished product. Initially, plastic pellets are heated until they soften. This is crucial, as the right temperature affects the final product's quality. The molten material is then injected into a mold. This mold shapes the plastic into the desired form. Precision here is vital; slight errors can lead to defects.
Once the plastic cools, it solidifies within the mold. At this stage, careful monitoring is needed. If the cooling time is off, the product may warp or crack. After cooling, the mold opens, and the finished item is ejected. However, this is not always seamless. Sometimes, parts stick to the mold, causing delays and requiring additional cleaning.
In the final phase, quality checks are performed. Products are examined for defects such as uneven surfaces or improper dimensions. These checks are crucial for ensuring that each item meets required standards. However, this step often reveals hidden flaws, prompting manufacturers to rethink their processes. Continuous improvement is essential in the plastic molding industry, as even minor mistakes can lead to significant waste.
What is a plastic molding machine and how does it work? - The Plastic Molding Process: Steps from Material to Final Product
| Step | Process Description | Materials Used | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Material Preparation | Plastic pellets, additives | Packaging, automotive components |
| 2 | Heating and Melting | Plastic resin | Consumer goods, electronic casings |
| 3 | Injection | Melted plastic | Toys, containers |
| 4 | Cooling | Solid plastic | Household items, automotive parts |
| 5 | Ejection | Finished molded part | Medical supplies, industrial components |
| 6 | Finishing | Various coatings and treatments | Consumer products, appliances |
Types of Plastic Molding Techniques Used in the Industry
Plastic molding is essential in manufacturing. There are several techniques employed in the industry. Each method serves unique applications and material types.
Injection molding is widely used. In this process, melted plastic is injected into a mold cavity. It cools and solidifies. This technique allows for precision and high production rates. It's ideal for complex shapes.
Blow molding is another common technique. It involves inflating hot plastic into a mold. This method creates hollow objects like bottles. It requires careful temperature control and timing.
Rotational molding is less common but useful. It involves rotating a mold filled with plastic powder. The heat causes the powder to coat the mold's interior. This creates strong, durable items. It's often used for larger products.
Tip: Consider the type of product you need. Each molding technique has pros and cons.
Thermoforming is also notable. It softens plastic sheets using heat. The sheets are then formed over molds. It's cost-effective for low-volume production.
Tip: Choose the right material. The final product's strength and flexibility depend on this choice.
Reflecting on these techniques highlights their importance. Each method has its challenges. Mastery of these processes is crucial for quality results.
Industry Statistics: Market Trends and Growth of Plastic Molding Machines
The market for plastic molding machines is evolving rapidly. Trends indicate that the demand for these machines is increasing. Various industries rely on them for shaping plastic materials into useful products. Packaging, automotive, and consumer goods are significant sectors driving growth. This surge is largely fueled by the rising use of plastics in everyday life.
In recent years, the industry has experienced a noticeable uptick in technological advancements. Automation and efficiency have become buzzwords. Machines now offer higher precision and speed. However, there are challenges. Not all manufacturers can keep pace with innovation. Investment in technology can be a barrier for smaller companies. Additionally, environmental concerns are also pushing the industry to reconsider materials.
Market statistics reveal shifts towards sustainable practices. Many companies are exploring biodegradable plastics. The transition may be slow but is essential. It poses questions about production processes. How can machines adapt to new materials? This is a critical reflection point for the industry moving forward. It is clear that while growth is promising, challenges require thoughtful solutions.
Related Posts
-
Top 10 Benefits of Plastic Molding for Your Manufacturing Needs
-

The Ultimate Guide to Acrylic Plastic Top Types for 2025
-

Top Benefits of Acrylic Sheets for Laser Cutting: Your Complete Guide
-

Discover the Benefits of Custom Cut to Size Plexiglass for Your Home and Business Needs
-

Mastering the Injection Molding Process: Tips for Streamlining Production Efficiency
-

How to Get Plexiglass Cut to Size for Your Projects and DIY Ideas
