Posts
What is Plastic Prototype Manufacturing? Benefits and Key Processes Explained
Plastic prototype manufacturing is a pivotal phase in the product development lifecycle, allowing designers and engineers to bring their concepts to life with tangible models. As industry expert Dr. Emily Carter, a leading voice in additive manufacturing, aptly puts it, "The ability to create precise plastic prototypes quickly not only accelerates the design process but also enhances collaboration among teams." This statement underscores the importance of plastic prototype manufacturing in fostering innovation and efficiency.
In an era where speed and accuracy are paramount, plastic prototype manufacturing offers a wide array of benefits, from cost-effectiveness to rapid iteration capabilities. It empowers businesses to test their ideas before committing to full-scale production, significantly reducing the likelihood of costly mistakes. Moreover, the processes involved in plastic prototype manufacturing, such as 3D printing and injection molding, are continually evolving, offering even more opportunities for customization and precision.
As we delve deeper into the benefits and key processes of plastic prototype manufacturing, we will explore how this technology is transforming industries and enabling companies to navigate the complexities of modern product development. Through a combination of expert insights and real-world applications, we aim to illuminate the vital role that plastic prototype manufacturing plays in shaping the future of design and production.
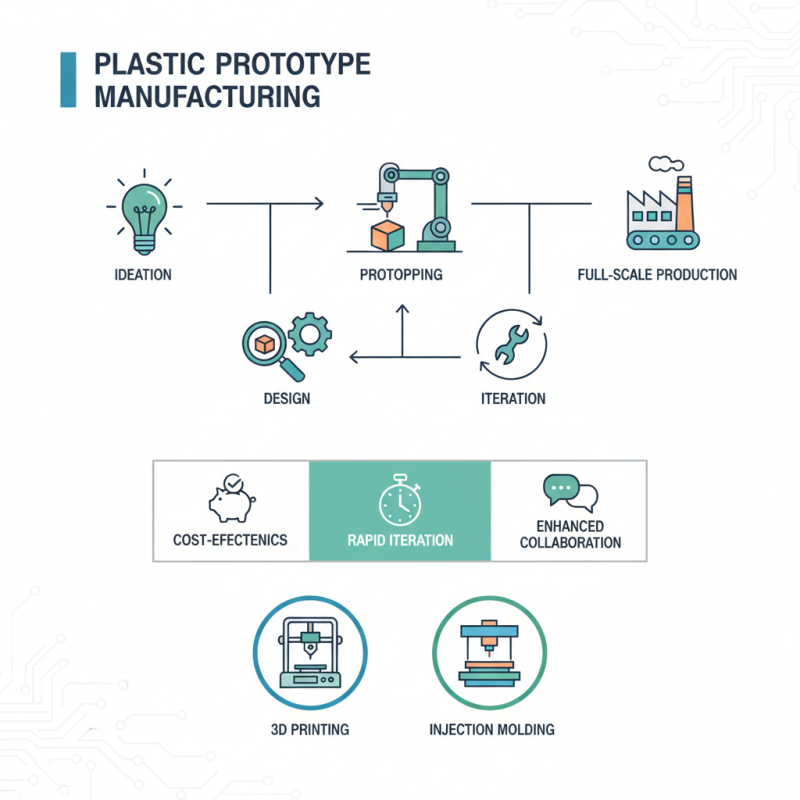
What is Plastic Prototype Manufacturing?
Plastic prototype manufacturing is a crucial process in product development, allowing businesses to create tangible models of their ideas before full-scale production. This method involves using various techniques such as injection molding, 3D printing, and CNC machining to fabricate prototypes from plastic materials. These prototypes serve as a vital tool for designers and engineers to test form, fit, and function, ensuring that the final product meets the intended specifications and requirements.
One of the key advantages of plastic prototype manufacturing is its ability to reduce development costs and time. By creating a physical model, teams can identify design flaws and make necessary adjustments early in the process, minimizing the risk of costly changes later on. Additionally, these prototypes can be used for user testing, providing valuable feedback that can drive improvements in the design. The versatility of plastic materials also allows for a wide range of finishes and colors, giving stakeholders a clearer vision of the final product and enhancing communication throughout the development cycle.
Key Benefits of Plastic Prototype Manufacturing

Plastic prototype manufacturing offers a multitude of benefits for businesses looking to innovate and refine their products before full-scale production. One of the primary advantages is the speed at which prototypes can be developed. With advancements in manufacturing technologies, such as 3D printing and CNC machining, companies can quickly create physical representations of their designs. This rapid prototyping not only accelerates the design process but also allows for efficient testing and revisions based on real-world feedback.
Additionally, plastic prototypes are cost-effective compared to traditional manufacturing methods. They minimize material waste and reduce the costs associated with mass production. By enabling businesses to test various designs and functionalities at a lower investment, plastic prototype manufacturing aids in identifying potential design flaws early in the development process. This leads to higher quality end products and can significantly shorten time-to-market, providing companies with a competitive edge in their industries. Overall, the ability to iterate quickly and efficiently, while keeping costs manageable, underscores the value of plastic prototype manufacturing in product development.
Essential Processes in Plastic Prototype Manufacturing
Plastic prototype manufacturing
is a crucial step in the product development process, offering essential benefits such as reduced time to market and the ability to evaluate design and functionality before mass production. Several key processes contribute to effective plastic prototype manufacturing, each with its own advantages.
One of the primary processes involved is 3D printing, particularly useful for creating intricate designs and components with speed and precision. According to a report from the Wohlers Associates 2021, the additive manufacturing market is projected to grow to $35.6 billion by 2024, showcasing the increasing reliance on 3D printing in various industries.
Another critical process is injection molding, which allows for the rapid production of high-quality prototypes. This technique is especially beneficial when creating durable parts and is known for its efficiency and scalability.
Tips:
When considering plastic prototype manufacturing, it's essential to select the appropriate material based on the prototype's intended function. Different plastics have varying properties, such as strength, flexibility, and temperature resistance, which can significantly impact the prototype's performance.
Moreover, collaborating closely with engineers during the design phase can help identify potential issues early, ultimately leading to a more successful final product.
Choosing the Right Techniques for Your Prototype
When selecting the right techniques for plastic prototype manufacturing, it’s essential to consider the specific requirements of your project. Different methods such as injection molding, 3D printing, and CNC machining offer unique advantages depending on factors such as complexity, production volume, and material properties. For instance, 3D printing is ideal for rapid prototyping due to its flexibility and speed, allowing designers to iterate quickly without the high initial costs associated with traditional methods. Conversely, injection molding is favored for larger production runs due to its efficiency and ability to create highly detailed parts.
Understanding the intended use of the prototype also plays a crucial role in the decision-making process. If the prototype is meant for functional testing, selecting a technique that accurately represents the end material and production process is vital. On the other hand, for visual or concept demonstrations, methods like vacuum forming or SLA (Stereolithography) may be more appropriate, as they can provide a high-quality finish with less focus on durability. Ultimately, making an informed choice about the manufacturing technique will significantly influence the time, cost, and effectiveness of bringing your prototype to life.
Plastic Prototype Manufacturing Processes and Benefits
Common Applications of Plastic Prototypes in Various Industries

Plastic prototypes play a crucial role in various industries by facilitating rapid product development and testing. In the automotive sector, for instance, plastic prototypes are used to create detailed components that can be tested for fit and functionality before mass production. This not only accelerates the design process but also allows manufacturers to identify potential issues early, reducing the risk of costly changes later in production.
In the consumer electronics industry, plastic prototypes are essential for both aesthetic and functional testing. Designers can create tactile models of gadgets to assess ergonomics and user interaction, ensuring that the final product meets consumer expectations. Additionally, in the medical field, plastic prototyping is used to develop tools and devices that require precise engineering, enabling healthcare professionals to validate designs for safety and effectiveness before they are brought to market. By leveraging plastic prototypes, industries can innovate more efficiently while ensuring quality and performance align with both regulatory standards and consumer needs.
Related Posts
-

Revolutionizing Product Design with Advanced Plastic Prototype Manufacturing Techniques
-

Why Plastic Prototype Manufacturing is Essential for Successful Product Development
-

How to Choose the Perfect Acrylic Sheets for Your Project
-

Top 10 Tips for Choosing the Best Plastic Board for Your Projects
-

Why Clear Plastic is the Perfect Choice for Your Packaging Needs
-

2025 Top 5 Colored Acrylic Sheets for Creative Projects and Designs
